Externalize Spring-Modulith Events with Spring Cloud Stream
While Spring Modulith provides multiple event externalizers, there are scenarios where you need more flexibility and control.
Spring Modulith enables developers to build well-structured modular monoliths with built-in event capabilities. This allows teams to leverage Event-Driven Architecture patterns without immediately committing to a distributed system.
It provides multiple event externalizers out-of-the-box:
- Kafka:
spring-modulith-events-kafka - AMQP:
spring-modulith-events-amqp - JMS:
spring-modulith-events-jms - AWS SQS:
spring-modulith-events-aws-sqs - AWS SNS:
spring-modulith-events-aws-sns - Spring Messaging:
spring-modulith-events-messaging
While these built-in externalizers cover common use cases, there are scenarios where you need more flexibility and control.
I'm happy to introduce a new library featuring a new Spring Modulith event externalizer for Spring Cloud Stream.
Why a New Library?
This library addresses several key needs by:
- Leverage Spring Cloud Stream to support multiple message brokers at once, even inside the same application.
- Providing enhanced control over message headers and metadata.
- Supporting flexible payload serialization with both JSON and Avro.
Getting Started
Using this library is straightforward. Here's what you need to do:
- Add the Spring-Modulith Events Externalizer dependency to your project
- Include your preferred Spring Cloud Stream binder (Kafka, RabbitMQ, etc.)
- Configure Spring Cloud Stream bindings in application.yml
- Enable externalization with
@EnableSpringCloudStreamEventExternalization - Use
ApplicationEventPublisheras normal, to publish POJOs, Avro orMessage<?>events
1. Add Core Dependency
<dependency><groupId>io.zenwave360.sdk</groupId><artifactId>spring-modulith-events-scs</artifactId><version>1.0.0-RC1</version></dependency>
2. Add Spring Cloud Stream Message Broker Binder
Choose your preferred message broker. For Kafka:
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-stream-binder-kafka</artifactId></dependency>
3. Configure Bindings
Configure your output bindings in application.yml. We are going to configure two output bindings for different payload types:
spring:cloud:stream:bindings:# JSON events bindingcustomers-json-out-0:destination: customers-json-topic# Avro events bindingcustomers-avro-out-0:destination: customers-avro-topiccontent-type: application/*+avro# Kafka-specific configurationkafka:producer:key-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
A key advantage of using Spring Cloud Stream is the ability to configure multiple message brokers simultaneously:
- Use different brokers (Kafka, RabbitMQ, etc.) in the same application
- Route different events to different brokers through configuration
Basic Configuration
Enable Spring Cloud Stream externalization by adding the @EnableSpringCloudStreamEventExternalization annotation:
@Configuration@EnableSpringCloudStreamEventExternalizationpublic class EventsConfiguration { }
Sending Events
POJO Events
Use ApplicationEventPublisher as you normally would in Spring Modulith:
@Externalized("customers-json-out-0::#{#this.getId()}") // binding name and routing keypublic class CustomerEvent {// Your POJO implementation}@Service@Transactionalpublic class CustomerEventsProducer {private final ApplicationEventPublisher publisher;public CustomerEventsProducer(ApplicationEventPublisher publisher) {this.publisher = publisher;}public void publishCustomerEvent(CustomerEvent event) {publisher.publishEvent(event); // <-- Sending the event}}
Avro Events
- Add the Avro dependency:
<dependency><groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId><artifactId>jackson-dataformat-avro</artifactId></dependency>
- Define your Avro event:
@Externalized("customers-avro-out-0::#{#this.getId()}") // binding name and routing keypublic class CustomerEvent extends SpecificRecordBase implements SpecificRecord {// Your Avro implementation}
- Publish events the same way as POJOs:
@Service@Transactionalpublic class CustomerEventsProducer {private final ApplicationEventPublisher publisher;public void publishAvroEvent(CustomerEvent event) {publisher.publishEvent(event); // <-- Sending the event}}
Routing Key Header
The SpringCloudStreamEventExternalizer automatically maps routing keys to the appropriate message header based on your message broker:
| Message Broker | Header Name |
|---|---|
| Kafka | kafka_messageKey |
| RabbitMQ | rabbit_routingKey |
| Kinesis | partitionKey |
| Google PubSub | pubsub_orderingKey |
| Azure Event Hubs | partitionKey |
| Solace | solace_messageKey |
| Apache Pulsar | pulsar_key |
Event Serialization for Spring Modulith Publication Log
Spring Modulith's Transactional Event Publication Log requires events to be serialized for database storage. This presents two challenges:
- Type Information: The default
JacksonEventSerializerloses generic type information forMessage<?>payloads - Format Support: If you need to support Avro payloads,
JacksonEventSerializerdoes not play well with Avro GenericRecord/SpecificRecord
This library addresses these challenges by:
- Adding a
_classfield to preserve complete type information forMessage<?>payloads - Supporting both POJO (JSON) and Avro serialization formats, through
AvroMapper - Enabling full deserialization back to original types
Avro serialization requires the com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.avro.AvroMapper class to be present in the classpath. In order to use Avro serialization, you need to add com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat:jackson-dataformat-avro dependency to your project, as stated above
Sending Spring Message Events
For advanced control over message headers, you can send Message<?> objects by including the spring.cloud.stream.sendto.destination routing header. This header should point to your intended Spring Cloud Stream output binding.
@Servicepublic class CustomerEventsProducer {private final ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher;public CustomerEventsProducer(ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher) {this.applicationEventPublisher = applicationEventPublisher;}@Transactionalpublic void sendCustomerEvent(CustomerEvent event) {Message<CustomerEvent> message = MessageBuilder.withPayload(event) // supports both POJO and Avro payloads.setHeader(SpringCloudStreamEventExternalizer.SPRING_CLOUD_STREAM_SENDTO_DESTINATION_HEADER,"customers-json-out-0" // target binding name).build();applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(message);}}
This header is automatically set when using ZenWave SDK AsyncAPI Generator.
Event Externalization and API Management with AsyncAPI
While Spring Modulith's @Externalized annotation provides a quick and convenient way to publish events, teams building event-driven systems often need additional capabilities:
- API Documentation: No built-in support for formal API documentation
- Schema Management: No friction to prevent breaking changes in event schemas that could impact consumers
- API Governance: No standardized way to enforce API design standards: naming conventions, versioning, headers/metadata...
API-First Approach with AsyncAPI
For teams following API-First practices, AsyncAPI offers a better approach to describe your Event-Driven Architecture:
- Formal API documentation
- Schema validation (Avro, JSON Schema)
- API governance and versioning
- Contract-first development
Code Generation with ZenWave SDK
The ZenWave SDK AsyncAPI Generator can generate full SDKs from AsyncAPI definitions, including:
- Event Models/DTOs with full type safety
- Strongly-typed header objects with runtime population support
- Spring Cloud Stream event producers/consumers with transactional support via Spring Modulith
- Zero boilerplate code
NOTE: Already using
@Externalized? We're developing a tool to reverse engineer your events into AsyncAPI specifications.
Example Implementation
See it in action with this complete example:
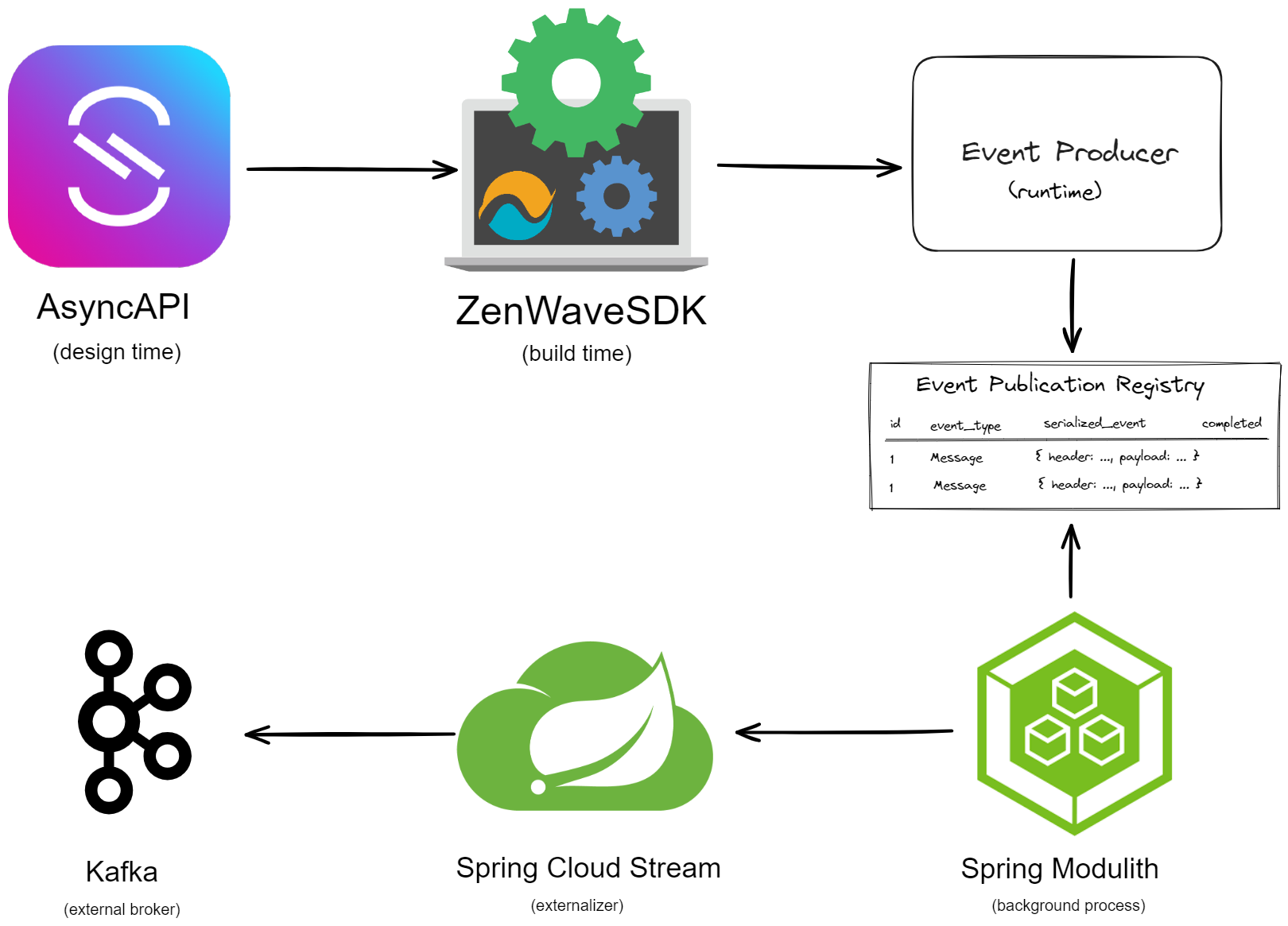
- Playground Project: Full implementation with AsyncAPI + Avro
- Implementation Guide: Step-by-step tutorial
Benefits Over Built-in Externalization
- Broker Flexibility: Connect to any message broker supported by Spring Cloud Stream
- Enhanced Header Control: Simple configuration of message headers
- Multiple Serialization Formats: Built-in support for JSON and Avro
- AsyncAPI Integration: Seamless integration with Spring Modulith Events and Spring Cloud Stream through ZenWave SDK AsyncAPI Generator
Get Involved
Visit GitHub repository
We welcome contributions and feedback from the community! 🚀
